A Complete Guide to Computer Networks: Key Insights & Essential Information
Computer networks are systems that allow devices to connect, communicate, and exchange information. These networks link computers, servers, mobile devices, sensors, and digital systems so they can share data and resources. At the core of every network is the concept of communication through established rules known as network protocols. Examples include TCP/IP, routing protocols, and DNS systems that support efficient data transfer.
Networks exist to make communication faster, improve resource sharing, and enable collaboration across different locations. Early networks focused on connecting small groups of computers, while modern network architecture supports millions of devices across local networks, cloud platforms, and global communication channels.
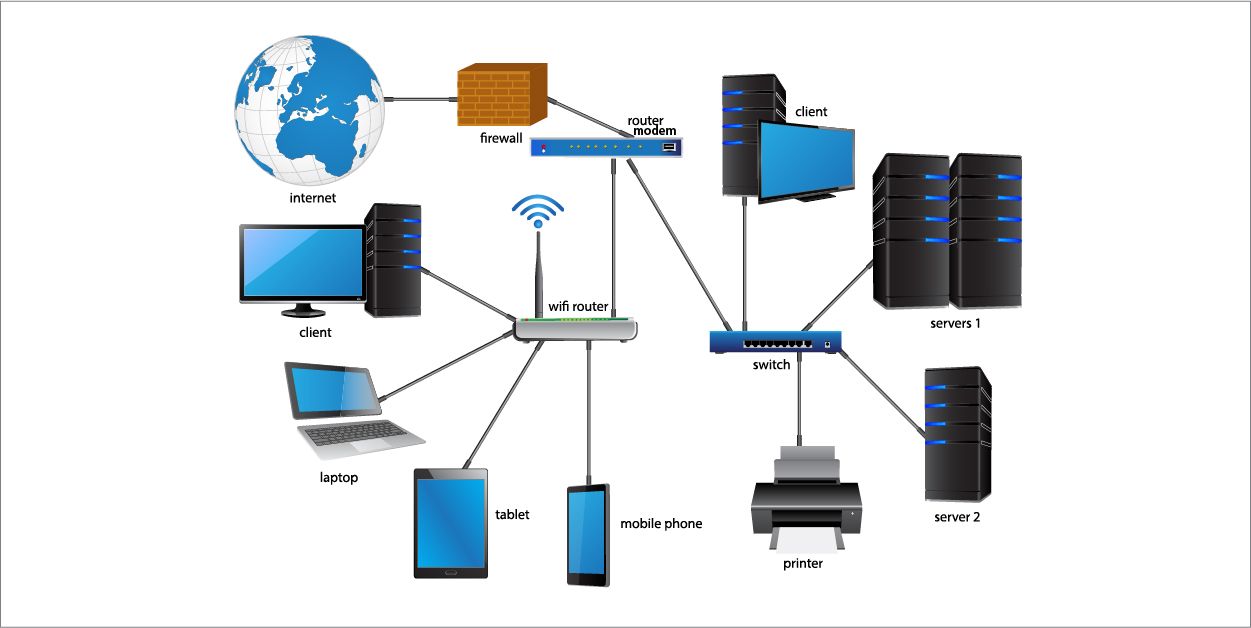
Today, computer networks support digital activities such as cloud networking, enterprise networks, wireless networking, IoT networks, and remote connectivity through technologies like VPN and SD-WAN. They form the backbone of data centers, online applications, digital storage, and cybersecurity frameworks.
Importance: Why Computer Networks Matter Today and What Problems They Solve
Computer networks play a central role in modern digital environments. Their importance continues to grow as organizations and individuals depend on connectivity for communication, information access, and secure data transfer.
Key reasons why computer networks matter include:
-
They enable real-time communication and collaboration across locations.
-
They support essential technologies such as cloud systems, data centers, and enterprise applications.
-
They allow resource sharing, reducing the need for isolated hardware.
-
They improve network security by providing controlled access, structured monitoring, and protection against unauthorized activities.
-
They support cybersecurity frameworks that safeguard digital assets.
-
They make digital services like streaming, messaging, and online platforms possible.
-
They enhance the functioning of IoT networks, where connected sensors collect and share information.
Problems that networks help solve:
-
Lack of connectivity between devices
-
Inefficient communication processes
-
Data storage limitations by enabling cloud networking
-
Security vulnerabilities through firewall systems and encryption
-
Difficulty managing large-scale digital systems without network monitoring tools
Who is affected by modern computer networks:
-
Students and educators learning core networking and cybersecurity
-
Organizations operating enterprise networks and data centers
-
Professionals managing network infrastructure and routing protocols
-
General users relying on wireless networking and internet access
-
Developers building applications that depend on stable network environments
Recent Updates: Key Trends and Changes in Computer Networks
Recent advancements have shaped how networks operate and evolve. Some of the most notable changes from the past year include:
-
Growth of AI-driven network monitoring tools that automate performance analysis and threat detection.
-
Increased integration of cloud networking to manage hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
-
Expansion of software-defined networking (SDN) and SD-WAN as organizations seek flexible routing and traffic control.
-
Rising adoption of Zero-Trust Network Architecture (ZTNA) as part of stronger cybersecurity strategies.
-
Enhancement of Wi-Fi standards, supporting faster data rates and improved wireless networking performance.
-
Growth in IoT networks, requiring more efficient protocols for device management and data handling.
-
Increased focus on network security and firewall systems as cyber threats continue evolving.
These updates emphasize automation, resilience, and secure connectivity across all kinds of network setups.
Laws or Policies Influencing Computer Networks
Computer networks are shaped by general regulatory principles that guide digital communication, cybersecurity, and data protection. While specific rules vary by region, the common areas of influence include:
-
Regulations related to digital privacy, ensuring safe handling of personal and organizational data.
-
Policies governing cybersecurity practices, including protection standards for network infrastructure.
-
Guidelines for data transmission, network reliability, and communication protocols.
-
Compliance requirements for secure access management, encryption usage, and unauthorized activity prevention.
-
Standards that define how network equipment should operate to maintain interoperability and safety.
These policies encourage secure connectivity, responsible data management, and reliable communication across all types of networks.
Tools and Resources for Learning and Managing Computer Networks
Below are tools, platforms, and resources commonly used to understand, design, and monitor networks.
Network Simulation and Learning Tools
-
Cisco Packet Tracer
-
GNS3
-
Wireshark
-
NetSim Labs
-
Network topology creators and visualizers
Network Infrastructure and Monitoring Tools
-
Network scanning utilities
-
Routing and switching configuration tools
-
Network monitoring dashboards
-
Traffic analysis software
-
Firewall and cybersecurity tools
Educational Resources
-
Networking protocol manuals
-
Cloud networking documentation
-
Online libraries covering LAN, WAN, VPN, SD-WAN, and wireless networking concepts
-
Network architecture reference guides
-
Cybersecurity and network security best-practice documents
These resources support both beginners and professionals seeking to understand network infrastructure, routing protocols, and modern connectivity systems.
Example Table: Key Network Types and Their Uses
| Network Type | Purpose | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| LAN | Connects devices in a limited area | High speed, internal communication |
| WAN | Links networks over large distances | Routing protocols, scalable connectivity |
| WLAN | Wireless local networking | Wi-Fi access, mobility |
| VPN | Secure remote connection | Encrypted data transfer |
| SD-WAN | Software-defined wide-area networking | Traffic optimization, flexible routing |
FAQs
What are the main components of a computer network?
Common components include switches, routers, servers, access points, cables, wireless systems, and network security tools such as firewalls.
How do routing protocols work?
Routing protocols identify the most efficient path for data to travel between networks. They analyze network topology and adjust routes to maintain reliability.
What is the difference between LAN and WAN?
A LAN connects devices within a small area like a home or building, while a WAN covers large distances and links multiple networks together.
Why is network security important?
Network security protects systems from unauthorized access, data breaches, and cyber threats. It involves firewalls, encryption, authentication, and monitoring tools.
What role does cloud networking play in modern systems?
Cloud networking enables flexible access to data and applications stored on remote servers, supporting scalability and reliable connectivity.
Conclusion
Computer networks form the foundation of modern digital communication. They allow devices to connect, share information, and operate efficiently across local and global environments. With advancements in network architecture, cybersecurity, cloud networking, and monitoring tools, networks continue evolving to support new technologies and expanded connectivity. Understanding these systems helps individuals and organizations navigate digital environments, protect data, and utilize essential tools that rely on stable and secure network infrastructure.
